Welcome to a quick tutorial on how to create a simple content management system (CMS) with PHP and MYSQL. Looking to challenge yourself or just want a really simple CMS for your current project? Well, an actual example will better explain things. Let us walk through one in this guide – Read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DOWNLOAD & NOTES
Here is the download link to the example code, so you don’t have to copy-paste everything.
EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
Just click on “download zip” or do a git clone. I have released it under the MIT license, so feel free to build on top of it or use it in your own project.
SORRY FOR THE ADS...
But someone has to pay the bills, and sponsors are paying for it. I insist on not turning Code Boxx into a "paid scripts" business, and I don't "block people with Adblock". Every little bit of support helps.
Buy Me A Coffee Code Boxx eBooks
BAREBONES CMS
All right, let us now get started with the barebones CMS in PHP and MYSQL.
TUTORIAL VIDEO
STEP 1) CONTENT DATABASE TABLE
CREATE TABLE `contents` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`title` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`text` text NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
ALTER TABLE `contents`
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
ADD KEY `title` (`title`),
ADD FULLTEXT KEY `text` (`text`);
ALTER TABLE `contents`
MODIFY `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT;| Field | Description |
id |
The content ID, primary key. |
title |
Title of the page. |
text |
The contents of the page itself. |
Yep, this one should be very straightforward, we need a table to store the title and content of the pages. Just a small note here though, the title and text are indexed – ADD KEY `title` and ADD FULLTEXT KEY `text`. This indexing will take up a little more disk space but greatly improves the search performance.
STEP 2) CMS CONTENT LIBRARY
<?php
class Content {
// (A) CONSTRUCTOR - CONNECT TO DATABASE
private $pdo;
private $stmt;
public $error;
function __construct () {
$this->pdo = new PDO(
"mysql:host=".DB_HOST.";dbname=".DB_NAME.";charset=".DB_CHARSET,
DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, [
PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE => PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION,
PDO::ATTR_DEFAULT_FETCH_MODE => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC
]);
}
// (B) DESTRUCTOR - CLOSE DATABASE CONNECTION
function __destruct () {
$this->pdo = null;
$this->stmt = null;
}
// (C) HELPER - RUN SQL QUERY
function query ($sql, $data=null) : void {
$this->stmt = $this->pdo->prepare($sql);
$this->stmt->execute($data);
}
// (D) SAVE CONTENT
function save ($title, $text, $id=null) {
if (is_numeric($id)) {
$sql = "REPLACE INTO `contents` (`id`, `title`, `text`) VALUES (?,?,?)";
$data = [$id, $title, $text];
} else {
$sql = "INSERT INTO `contents` (`title`, `text`) VALUES (?,?)";
$data = [$title, $text];
}
$this->query($sql, $data);
return true;
}
// (E) LOAD CONTENT
function load ($id) {
$this->query("SELECT * FROM `contents` WHERE `id`=?", [$id]);
return $this->stmt->fetch();
}
// (F) SEARCH CONTENT
function search ($search) {
$this->query("SELECT * FROM `contents` WHERE `title` LIKE ? OR `text` LIKE ?", ["%$search%", "%$search%"]);
return $this->stmt->fetchAll();
}
}
// (G) DATABASE SETTINGS - CHANGE THESE TO YOUR OWN!
define("DB_HOST", "localhost");
define("DB_NAME", "test");
define("DB_CHARSET", "utf8mb4");
define("DB_USER", "root");
define("DB_PASSWORD", "");
// (H) CREATE NEW CONTENT OBJECT
$_CMS = new Content();The core library may look a little intimidating at first, but keep calm and look carefully.
- (A, B, G) On creating
$_CMS = new Content(), the constructor will automatically connect to the database; The destructor closes the connection when the object is destroyed. - (C)
query()A helper function to run an SQL query. - (D to F) There are only 3 “content functions” here.
save()To save page contents.load()To get the page contents.search()Search page contents.
- (G) Remember to change the database settings to your own.
That’s all, feel free to expand and add more of your own functions – Delete content, advanced search, save to HTML file, etc…
STEP 3) UPDATE CONTENT PAGE
<!-- (A) TINY MCE -->
<!-- https://www.tiny.cloud/ -->
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/tinymce/6.7.1/tinymce.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = () => tinymce.init({
selector : "#mce",
menubar : false,
plugins: "lists link",
toolbar: "bold italic underline | forecolor | bullist numlist | alignleft aligncenter alignright alignjustify | link"
});
</script>
<?php
// (B) LOAD LIBRARY
require "2-lib.php";
$id = 1; // fixed to 1 for simplicity
// (C) SAVE CONTENT WHEN FORM IS SUBMITTED
if (isset($_POST["title"])) {
echo $_CMS->save($_POST["title"], $_POST["text"], $id)
? "<div class='note'>CONTENT UPDATED</div>"
: "<div class='note'>".$_CMS->error."</div>" ;
}
// (D) EDIT PAGE
$content = $_CMS->load($id); ?>
<form method="post">
<label>Title</label>
<input type="text" name="title" required value="<?=$content==false?"":$content["title"]?>">
<label>Content</label>
<textarea id="mce" name="text"><?=$content==false?"":$content["text"]?></textarea>
<input type="submit" value="Save">
</form>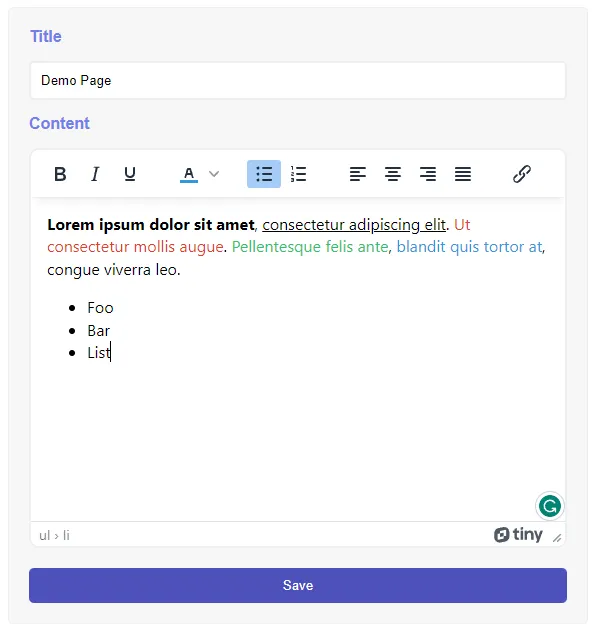
Right, this page is seemingly complicated again, but let’s walk through it:
- Load TinyMCE (a WYSIWYG editor) from the CDN.
- Self-explanatory. Load the PHP library, but we fix the content ID to
$id = 1in this demo to keep things simple. - Save the content when the form is submitted.
- HTML form to update the content itself.
That’s all for the essentials behind this “one-page admin”.
STEP 4) DISPLAY CONTENT PAGE
<?php
// (A) GET PAGE CONTENTS FROM DATABASE
require "2-lib.php";
$id = 1; // fixed to 1 for simplicity
$content = $_CMS->load($id);
// (B) OUTPUT HTML ?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title><?=$content["title"]?></title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="0-dummy.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1><?=$content["title"]?></h1>
<main><?=$content["text"]?></main>
</body>
</html>
Now that we have some dummy contents in the database, the final step is to output it… This should not be a mystery anymore. We simply use $content = $_CORE->load($id) to fetch and output the contents.
EXTRAS
That’s all for this guide, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
MORE IMPROVEMENT IDEAS
This example works, but it is only a barebones system. It is far from a “complete professional system”, here are a couple more “good stuff” you can consider adding:
- Protect
3-save.php. Create a user login system and admin panel – Check out the links below. - Change
4-load.phpto also load different pages, create your own HTML template. - If you want a “pretty URL system” like WordPress or Drupal, feel free to add a “URL” field in the database. You will also need to work with
htaccess, check out the pretty URL link below. - Add a file manager to your CMS, do a search for “PHP file manager” on the Internet.
HOW ABOUT MULTIPLE PAGES?
As for “how to manage multiple pages”, everyone has different requirements and starting points. So I will not go into the exact details, here is a lazy way:
- Add a
getAll()function in2-lib.php,SELECT `id`, `title` FROM `contents`. - Use
getAll()to build an admin page that lists all the available content. - When the administrator clicks on a page in the list, redirect to
3-save.php?id=N. - The rest should be straightforward. Modify
3-save.phpand4-load.phpto load the content with$_GET["id"]instead.
LINKS & REFERENCES
- Simple Admin Panel – Code Boxx
- PHP Pretty URL With HTACCESS – Code Boxx
- MYSQL Search Queries (Exact vs Like vs Fuzzy) – Code Boxx
THE END
Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope that it has helped you with your project, and if you want to share anything with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy coding!

Perfect! Thank You!