Welcome to a beginner’s tutorial on working with sessions in PHP. So you have heard of this session thing, and trying to figure out how it works? Let us walk through some super simple examples in this guide – Read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DOWNLOAD & NOTES
Here is the download link to the example code, so you don’t have to copy-paste everything.
EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
Just click on “download zip” or do a git clone. I have released it under the MIT license, so feel free to build on top of it or use it in your own project.
SORRY FOR THE ADS...
But someone has to pay the bills, and sponsors are paying for it. I insist on not turning Code Boxx into a "paid scripts" business, and I don't "block people with Adblock". Every little bit of support helps.
Buy Me A Coffee Code Boxx eBooks
PHP SESSIONS
All right, let us now get into the examples of working with sessions in PHP.
WHAT IS A SESSION?
What the heck is a “session”?
- PHP variables are temporary – They “disappear” and “cannot be carried onto another page”.
- Sessions are a way to “save user data”, and allow data to persist over multiple pages.
PART 1) START/RESUME SESSION
1A) PHP SESSION START
<?php
// (A) START SESSION
session_start();
// (B) SESSION VARIABLES
$_SESSION["hello"] = "world";
$hello = "world";
// (C) OUTPUT
print_r($_SESSION); // ["hello" => "world"]
echo $hello; // "world"- To start a session, call
session_start(). - Just assign whatever you want to keep into
$_SESSION["KEY"] = "VALUE". - Here, we have assigned both
$_SESSION["hello"] = "world"and$hello = "world".
1B) RESUME SESSION
<?php
// (A) START/RESUME SESSION
session_start();
// (B) OUTPUT
print_r($_SESSION); // ["hello" => "world"]
echo $hello; // gone - undefined variable- To resume the session, call the same old
session_start(). - As demonstrated, the session still contains
$_SESSION["hello"] = "world", but$hellohas perished at the end of1a-start.php.
PART 2) APPEND DATA TO THE SESSION
<?php
// (A) START/RESUME SESSION
session_start();
// (B) APPEND TO SESSION
$_SESSION["name"] = "Jon Doe";
$_SESSION["colors"] = ["Red", "Green", "Blue"];
// (C) OUTPUT
print_r($_SESSION); // [hello, name, colors]No sweat. Just use $_SESSION like a “normal array” and assign more keys/values to it.
PART 3) SESSION CAN ONLY CONTAIN KEY/VALUE PAIRS
<?php
// (A) START/RESUME SESSION
session_start();
// (B) BAD WAYS TO ASSIGN SESSION VALUES
// $_SESSION = "hello";
// $_SESSION = 123;
// $_SESSION = ["hello", "world"];Take extra note that $_SESSION is a “special variable”, and it can only accept $_SESSION["KEY"] = "VALUE" pairs.
- If you assign a flat string or number into
$_SESSION, it will only work for the current script.- That is,
$_SESSION = "hello". echo $_SESSIONwill give you"hello"for the current script.- But in another script,
$_SESSIONwill “restore” to its “last valid keys/values” state.
- That is,
- If you assign an indexed array
$_SESSION = [1, 2, 3], PHP will outright throw a warning.
PART 4) UNSETTING SESSION DATA
<?php
// (A) START/RESUME SESSION
session_start();
// (B) SET SESSION VARIABLES
$_SESSION = [
"name" => "Jon",
"age" => 999,
"gender" => "Male"
];
print_r($_SESSION); // [name, age, gender]
// (C) UNSET
unset($_SESSION["age"]);
print_r($_SESSION); // [name, gender]
To remove certain data from the session, simply unset($_SESSION["KEY"]).
PART 5) END SESSION
<?php
// (A) START/RESUME SESSION
session_start();
print_r($_SESSION);
// (B) END SESSION
session_destroy();
unset($_SESSION);
print_r($_SESSION); // cleared - undefined
- To end a session, use
session_destroy(). - Take extra note – Data inside
$_SESSIONwill still remain until the end of the current script. If you want to “fully destroy” the current session immediately, you will have to callunset($_SESSION).
EXTRAS
That’s all for the tutorial, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
HOW DO SESSIONS WORK?
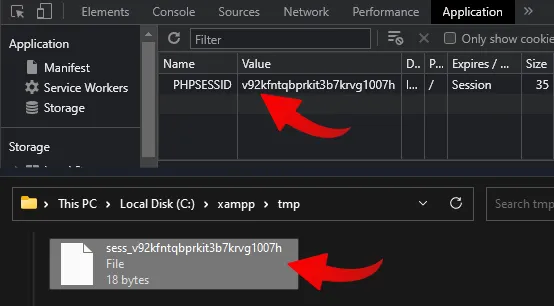
To shed some light on the technical backend here. When session_start() is called:
- PHP will generate a
PHPSESSIDunique ID cookie. - A corresponding
sess_PHPSESSIDfile will also be created on the server.
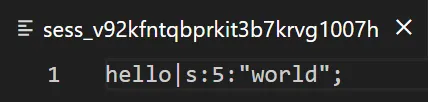
So whenever we assign $_SESSION["KEY"] = "VALUE", it will be saved into the sess_PHPSESSID file. For those who are lost, it will be easier to think of sess_PHPSESSID as a “save game file”; Data is restored from this file whenever the user revisits the webpage.
SESSION RESTRICTIONS
- Take note that sessions have an expiry time as set in
session.cookie_lifetimeofphp.ini. - If the user clears the cookies, the session will also be lost.
- Sessions are file-based. If you are working with distributed servers, this may end up with some trouble (unless you have a way to share the session file across different servers). Consider setting the session to save into a database instead. See the “cross-domain session” link below.
REFERENCES & LINKS
- Session Super Global – PHP
- Start Session – PHP
- Destroy Session – PHP
- Cross-Domain Session – Code Boxx
- Save PHP Session In Database – Code Boxx
THE END
Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope that it has helped you to better understand, and if you want to share anything with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy coding!

Great Job