Welcome to a tutorial on how to create a simple online contact form with Python Flask. So you want to create a contact form, but don’t want to deal with Django or all the crazy database stuff? Well, here’s a quick alternative with Flask – Read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DOWNLOAD & NOTES
Here is the download link to the example code, so you don’t have to copy-paste everything.
EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
Just click on “download zip” or do a git clone. I have released it under the MIT license, so feel free to build on top of it or use it in your own project.
SORRY FOR THE ADS...
But someone has to pay the bills, and sponsors are paying for it. I insist on not turning Code Boxx into a "paid scripts" business, and I don't "block people with Adblock". Every little bit of support helps.
Buy Me A Coffee Code Boxx eBooks
PYTHON CONTACT FORM
All right, let us now get into the details of building a contact form with Python Flask. Not going to explain line-by-line, but here’s a quick walkthrough.
QUICK SETUP
- Create a virtual environment
virtualenv venvand activate it –venv\Scripts\activate(Windows)venv/bin/activate(Linux/Mac) - Install required libraries –
pip install flask - For those who are new, the default Flask folders are –
staticPublic files (JS/CSS/images/videos/audio)templatesHTML pages
STEP 1) CONTACT PAGE
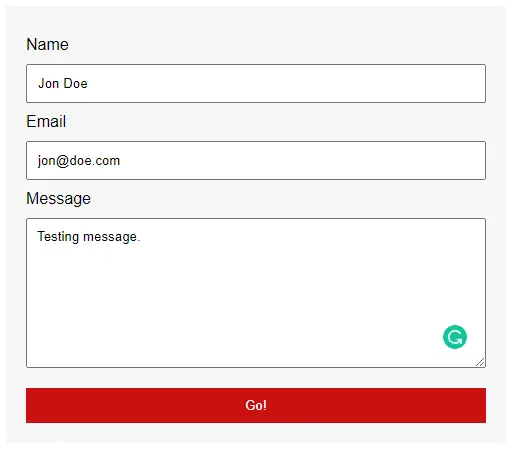
1A) HTML CONTACT FORM
<form id="contactForm" onsubmit="return send();">
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input type="text" name="Name" required>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input type="email" name="Email" required>
<label for="message">Message</label>
<textarea name="Message" required></textarea>
<input type="submit" value="Go!" id="contactGo">
</form>The first step should be self-explanatory. There’s nothing “special” here, this is just a simple HTML contact form. Feel free to change this form and add your own required fields.
1B) THE JAVASCRIPT
// (A) SEND CONTACT FORM
function send () {
// (A1) PREVENT MULTIPLE SUBMIT
document.getElementById("contactGo").disabled = true;
// (A2) COLLECT FORM DATA
let data = new FormData(document.getElementById("contactForm"));
// (A3) SEND!
fetch("/book", { method:"POST", body:data })
.then(res => {
if (res.status==200) { location.href = "/thank"; }
else {
console.log(res);
alert("Opps an error has occured.");
}
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
alert("Opps an error has occured.");
});
return false;
}Next, we have a small bit of Javascript to handle the form submission.
- (A1) Disable the “submit” button to prevent multiple submissions.
- (A2 & A3) Collect the contact form, and send it to the server side with AJAX fetch post.
STEP 2) THANK YOU PAGE
<h1>Thank You</h1>
<p>We have received your contact request</p>A dummy “thank you page” on successful contact form submission. Once again, feel free to add your own message here.
STEP 3) SERVER-SIDE FORM HANDLING
3A) INITIALIZE
# (A) INIT
# (A1) LOAD REQUIRED PACKAGES
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, make_response
from werkzeug.datastructures import ImmutableMultiDict
import smtplib
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
# (A2) FLASK INIT
app = Flask(__name__)
# app.debug = True
# (B) SETTINGS
HOST_NAME = "localhost"
HOST_PORT = 80
MAIL_FROM = "sys@site.com"
MAIL_TO = "admin@site.com"
MAIL_SUBJECT = "Contact Form"The first few sections of the server side are nothing more than loading the required packages and defining the settings. A reminder here to change the settings to your own, especially the email.
3B) ROUTES – HTML PAGES
# (C) ROUTES
# (C1) CONTACT FORM
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template("S1A_contact.html")
# (C2) THANK YOU PAGE
@app.route("/thank")
def thank():
return render_template("S2_thank.html")Don’t think this needs much explanation:
http://localhost/to serve the contact formS1A-contact.html.http://localhost/thankto serve the “thank you” pageS2_thank.html.
3C) CONTACT FORM SUBMISSION
# (C3) SEND CONTACT FORM
@app.route("/send", methods=["POST"])
def foo():
# EMAIL HEADERS
mail = MIMEMultipart("alternative")
mail["Subject"] = MAIL_SUBJECT
mail["From"] = MAIL_FROM
mail["To"] = MAIL_TO
# EMAIL BODY (BOOKING DATA)
data = dict(request.form)
msg = "<html><head></head><body>"
for key, value in data.items():
msg += key + " : " + value + "<br>"
msg += "</body></html>"
mail.attach(MIMEText(msg, "html"))
# SEND MAIL
mailer = smtplib.SMTP("localhost")
mailer.sendmail(MAIL_FROM, MAIL_TO, mail.as_string())
mailer.quit()
# HTTP RESPONSE
res = make_response("OK", 200)
return res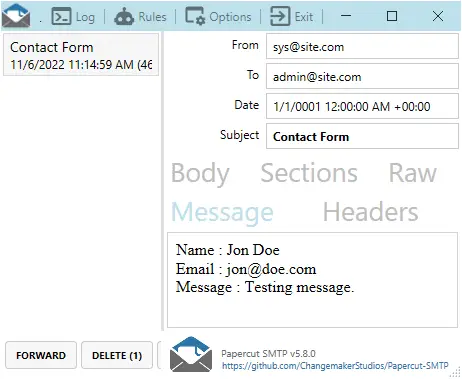
Remember that the Javascript will “send the contact form via AJAX fetch”? This part handles the form submission – Collects the form data, and sends it to the email address that you have specified.
3D) START!
# (D) START!
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(HOST_NAME, HOST_PORT)Finally, Captain Obvious at your service – This starts the HTTP web server.
EXTRAS
That’s all for the tutorial, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
EXTRA) MAIL SEND
Please take note that we are using mailer = smtplib.SMTP("localhost") to send emails. If your server is running Mac/Linux, things should work fine as long as sendmail is in place. But for Windows users, I will recommend installing Papercut SMTP for easy testing.
P.S. We can also configure smtplib to use a remote SMTP server. Just read their documentation.
THE END
Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end. I hope that it has helped you to better understand, and if you want to share anything with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy coding!
