Welcome to a tutorial on how to import an Excel file into the database in Python. So you have an Excel file that needs to “go into” a database? Well, it’s a simple process of reading the Excel file and importing it into the database – Read on for the example!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DOWNLOAD & NOTES
Here is the download link to the example code, so you don’t have to copy-paste everything.
EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
Just click on “download zip” or do a git clone. I have released it under the MIT license, so feel free to build on top of it or use it in your own project.
SORRY FOR THE ADS...
But someone has to pay the bills, and sponsors are paying for it. I insist on not turning Code Boxx into a "paid scripts" business, and I don't "block people with Adblock". Every little bit of support helps.
Buy Me A Coffee Code Boxx eBooks
PYTHON IMPORT EXCEL INTO DATABASE
All right, let us now get into the example of importing an Excel file in Python.
QUICK SETUP
- Create a virtual environment
virtualenv venvand activate it –venv\Scripts\activate(Windows)venv/bin/activate(Linux/Mac) - Install required libraries –
pip install openpyxl - For those who are new, the default Flask folders are –
staticPublic files (JS/CSS/images/videos/audio)templatesHTML pages
STEP 1) DUMMY DATABASE
1A) USERS’ TABLE
CREATE TABLE users (
uid INTEGER,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL,
tel TEXT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY("uid" AUTOINCREMENT)
);For this example, we will be working with a simple users’ table.
uidUser ID. Primary key and auto-increment.nameThe user’s full name.emailThe user’s email address.telUser’s telephone number.
1B) CREATE THE DATABASE
# (A) LOAD PACKAGES
import sqlite3, os
from sqlite3 import Error
# (B) DATABASE + SQL FILE
DBFILE = "users.db"
SQLFILE = "S1A_users.sql"
# (C) DELETE OLD DATABASE IF EXIST
if os.path.exists(DBFILE):
os.remove(DBFILE)
# (D) IMPORT SQL
conn = sqlite3.connect(DBFILE)
with open(SQLFILE) as f:
conn.executescript(f.read())
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print("Database created!")To keep things simple without having to install anything else, we will be using SQLite – This script will create users.db and import S1A_users.sql to create the users table.
PART 2) DUMMY EXCEL
| Jo Doe | jo@doe.com | 465785 |
| Joa Doe | joa@doe.com | 123456 |
| Job Doe | job@doe.com | 234567 |
| Joe Doe | joe@doe.com | 345678 |
| Jog Doe | jog@doe.com | 578456 |
| Joh Doe | joh@doe.com | 378945 |
| Joi Doe | joi@doe.com | 456789 |
| Jon Doe | jon@doe.com | 987654 |
| Jor Doe | jor@doe.com | 754642 |
| Joy Doe | joy@doe.com | 124578 |
Next, we have a whole bunch of users in an Excel to import into the users table.
PART 3) IMPORT EXCEL INTO THE DATABASE
# (A) INIT
# (A1) LOAD MODULES
import sqlite3, os
from sqlite3 import Error
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# (A2) SETTINGS
DBFILE = "users.db"
# (B) OPEN DATABASE & EXCEL FILE
conn = sqlite3.connect(DBFILE)
cursor = conn.cursor()
book = load_workbook("S2_users.xlsx")
sheet = book.active
# (C) IMPORT ROWS & COLUMNS
for row in range(1, sheet.max_row + 1):
sql = "INSERT INTO `users` (`name`, `email`, `tel`) VALUES "
sql += f"('{sheet.cell(row, 1).value}', '{sheet.cell(row, 2).value}', '{sheet.cell(row, 3).value}')"
cursor.execute(sql)
print(sql)
conn.commit()
conn.close()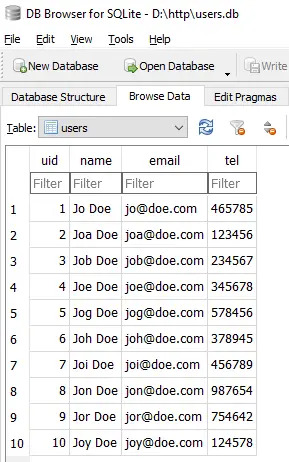
Lastly, I don’t think this needs a line-by-line explanation… This is doing the exact “read Excel file and import them into database”. But just one thing though – Python cannot read Excel files natively, so we are using openpyxl here. Read their documentation if you want to learn more, links below.
EXTRAS
That’s all for the tutorial, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
HOW ABOUT MYSQL, MSSQL, MONGODB, ETC…
There are a ton of databases in the world, this tutorial will never end if I went through each and every one. So this is your homework – Go through the basics of the database on your own, install your own preferred database management tool, change the SQL for the users table, and update s4_import.py to connect to the database of your choice instead.
IMPORT EFFICIENCY
A quick note that while the above example works, importing line-by-line is also very inefficient. So I will leave this as “another homework exercise” – Change the insertion to do by batches of 5 instead. That is, INSERT INTO `users` (`name`, `email`, `tel`) VALUES (ROW), (ROW), (ROW), (ROW), (ROW)
Shouldn’t be too difficult. Just introduce a count flag to “hold off” cursor.execute(sql) until there are 5 entries.
LINKS & REFERENCES
THE END
Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end. I hope that it has helped you to better understand, and if you want to share anything with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy coding!
